Verilog 代码生成工具分析
https://github.com/aichipdesign/chipgptv
该仓库代码很学术。大概逻辑就是把verilog 的端口描述作为 prompt 文件交给大模型去补全,多模态指用视觉大模型去读图片。我在通读 changkaiyan 学长等人的实现后,完成了一个最小实现,包含调取大模型根据电路描述文件生成 verilog 代码并且调用 iverilog 对 verilog 和 testbench 进行测试与验证,并且在过程中对用户进行友好的交互。
可以简单优化的地方
-
并行提交需求
-
使用环境变量来保存
openai api key -
可以添加日志功能
-
曾经使用的 openai model 已经下线需要更改
-
文件路径硬编码需要优化
整体功能
这是一个命令行工具,用于通过大语言模型 (LLM) 生成 Verilog 硬件描述语言 (HDL) 代码,支持三种不同的生成方法。
核心组件
-
命令行参数 (
main.py: 12-16)
- —model_name: 指定使用的模型名称(默认: “gpt-4.1”)
- —prompt_type: 提示类型(默认: “complex”)
- —method: 生成方法,支持三种模式:
-
Default: 标准代码生成
-
Complete: 代码补全模式 “ - Predict: token 预测模式
-
- 测试用例列表 (
main.py: 19-53)
包含 3 类硬件电路设计:
- 算术电路: 累加器 (accu)、加法器、除法器、乘法器等
- 数字电路: ALU、边缘检测、分频器、计数器、多路复用器等
- 高级电路: 状态机 (FSM)、流水线、片上网络等
目前只启用了 arithmetic/accu,其他都被注释掉了。
- 迭代次数 (
main.py:56)
Iter = {“default”: 5, “complete”: 3, “predict”: 3} 不同方法的重复生成次数不同。
- 主循环逻辑 (
main.py: 72-97)
对每个测试实例进行多次迭代生成:
- 输出路径构建: 根据 method 类型创建不同的输出目录
- 目录创建 (
main.py: 88-89): 确保输出目录存在 - 调用生成函数:
- Default: 调用 llm_generate_code () 生成完整代码
- Complete: 调用 llm_complete_code () 进行代码补全
- Predict: 调用 llm_predict_token () 进行 token 预测
输出文件结构
生成两类文件:
- .v 文件: Verilog 源代码
- .txt 文件: 可能是答案或元数据
路径格式如:
generated_code/{model_name}-{prompt_type}/{instance}_{iteration}.v工作目录设置
main.py: 7 将工作目录切换到项目根目录,确保相对路径正确。这个脚本的设计目的是系统化地测试 LLM 在硬件代码生成任务上的性能表现。
-
测试功能
我重新构建了一个最小实现(包含 changkaiyan 学长仓库中的从生成到利用 iverilog 将大模型生成的代码与 testbench 进行测试的最小实现)
运行如图
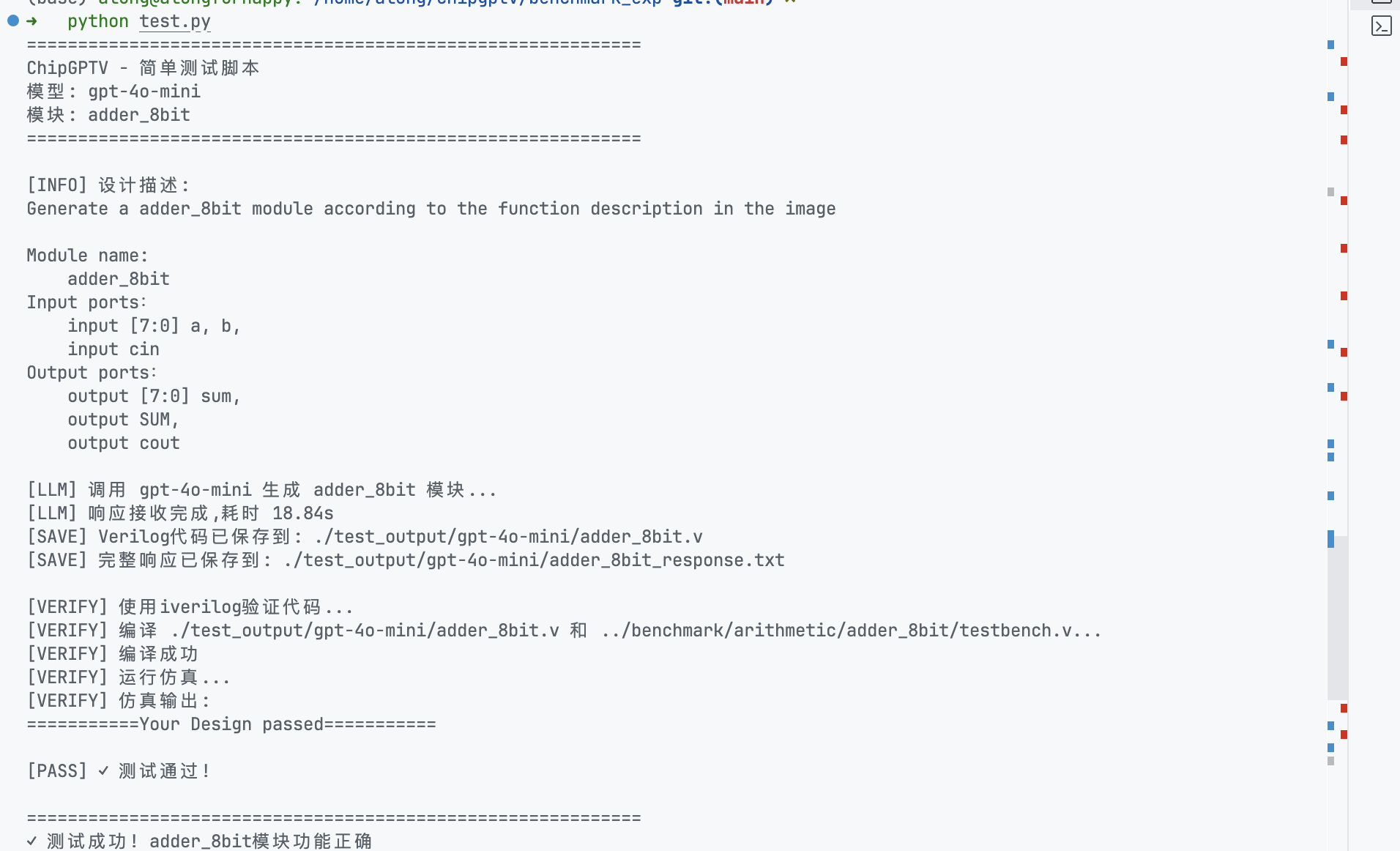
完整的最小实现代码在这里可以看到 https://github.com/Dragonzhoulong/chipgptv/blob/main/benchmark_exp/test.py
测试代码如下
def verify_with_iverilog(verilog_file, testbench_file, timeout=5):
"""
使用iverilog编译并运行测试
Args:
verilog_file: 生成的Verilog文件路径
testbench_file: testbench文件路径
timeout: 仿真超时时间(秒)
Returns:
(success, output): success为True表示测试通过,output为测试输出
"""
print(f"[VERIFY] 使用iverilog验证代码...")
# 临时输出文件
output_file = "test_output.vvp"
try:
# 步骤1: 编译
print(f"[VERIFY] 编译 {verilog_file} 和 {testbench_file}...")
compile_result = subprocess.run(
["iverilog", "-o", output_file, verilog_file, testbench_file],
capture_output=True,
text=True,
timeout=10
)
if compile_result.returncode != 0:
print(f"[FAIL] 编译失败:")
print(compile_result.stderr)
return False, compile_result.stderr
print(f"[VERIFY] 编译成功")
# 步骤2: 运行仿真
print(f"[VERIFY] 运行仿真...")
sim_result = subprocess.run(
["vvp", output_file],
capture_output=True,
text=True,
timeout=timeout
)
output = sim_result.stdout
print(f"[VERIFY] 仿真输出:")
print(output)
# 检查是否通过测试
if "Your Design passed" in output:
print(f"[PASS] ✓ 测试通过!")
return True, output
else:
print(f"[FAIL] ✗ 测试失败")
return False, output
except subprocess.TimeoutExpired:
print(f"[FAIL] 仿真超时")
return False, "Timeout"
except FileNotFoundError as e:
print(f"[ERROR] 找不到iverilog/vvp工具: {e}")
print(f" 请确保已安装Icarus Verilog: https://bleyer.org/icarus/")
return False, str(e)
except Exception as e:
print(f"[ERROR] 验证过程出错: {e}")
return False, str(e)
finally:
# 清理临时文件
if os.path.exists(output_file):
os.remove(output_file)
手动验证
(base) along@alongforhappy: /home/along/chipgptv/benchmark_exp git:(main) ✗
➜ iverilog -o test_output.vvp test_output/gpt-4o-mini/adder_8bit.v ../benchmark/arithmetic/adder_8bit/testbench.v
(base) along@alongforhappy: /home/along/chipgptv/benchmark_exp git:(main) ✗
➜ vvp
vvp: no input file.
(base) along@alongforhappy: /home/along/chipgptv/benchmark_exp git:(main) ✗
➜ vvp test_output.vvp
===========Your Design passed===========